Collaborative learning is all about students working together to achieve shared goals. It’s not just about group work—it’s about meaningful interaction that helps students learn better. When students collaborate effectively, they engage more with the material and with each other, which leads to better outcomes for everyone. This guide will show you how to use collaborative learning strategies to improve classroom interaction and make learning more engaging and effective.
What is Collaborative Learning
Collaborative learning is a teaching method where students work together in small groups to achieve a common goal. Instead of learning individually, students actively share ideas, discuss concepts, and support each other’s understanding of the material. This approach emphasizes teamwork and student participation, moving away from traditional teacher-centered instruction.
In collaborative learning, students are often grouped in pairs or small teams. They engage in joint intellectual efforts, whether searching for solutions, exploring new ideas, or creating projects. These activities focus on students interacting with the course material in a hands-on way, rather than just passively listening to lectures.
This method represents a shift from the conventional model where the teacher is the central source of knowledge and students primarily listen and take notes. Instead, teachers adopting collaborative learning approaches act more as facilitators or coaches. They design engaging and interactive learning experiences, guiding students through their exploration and application of the material. This encourages deeper understanding and more active involvement in the learning process.
Key Principles of Collaborative Learning
- Shared responsibility: In collaborative learning, every student in the group is responsible for contributing to the task. This creates a sense of accountability and encourages students to work together effectively.
- Active engagement: Students are actively involved in their learning. They ask questions, explain their thinking, and engage in discussions with their peers, which helps deepen their understanding of the subject.
- Diverse perspectives: Collaboration brings together different viewpoints. When students work in groups, they learn to consider ideas that may be different from their own, leading to a richer learning experience.
- Communication and interaction: Collaborative learning promotes strong communication skills. Students must articulate their thoughts clearly, listen to others, and build on each other’s ideas to solve problems or complete tasks.
Why Use Collaborative Learning?
Collaborative learning is used because it helps students learn better by working together. When students share ideas and help each other, they can understand the material more deeply. This method also builds important skills like teamwork, communication, and problem-solving, which are useful in real life.
By discussing and explaining things to each other, students can see different viewpoints and clear up any confusion they might have. Working in groups also makes learning more enjoyable and engaging, as students are more involved in the process. Instead of just listening to the teacher, they take an active role in their own learning.
What Are Collaborative Learning Strategies?
Collaborative learning strategies are methods or approaches used by educators to help students work together in groups to achieve common learning goals. These strategies are designed to encourage interaction, teamwork, and the sharing of ideas among students. The focus is on learning as a collective process, where students help each other understand concepts and solve problems, rather than just working individually.
Key Components of Collaborative Learning Strategies
- Group work: Students are divided into small groups to work on tasks or projects together. The size of the group can vary, but it’s usually kept small enough to ensure that everyone participates.
- Shared goals: Each group is given a clear, common goal that they need to achieve together. This could be completing a project, solving a problem, or understanding a specific concept.
- Interdependence: Students rely on each other to succeed. Each member of the group has a role or responsibility, and their contributions are crucial to the group’s overall success. This creates a sense of accountability within the group.
- Active participation: Collaborative learning strategies require all students to be actively involved. Whether it’s discussing ideas, solving problems, or presenting their work, everyone has a role to play.
- Teacher as a facilitator: The teacher guides the learning process, providing support and direction when needed, but allowing students to take the lead. The teacher’s role is to encourage collaboration and ensure that the group is working effectively.
Benefits of Collaborative Learning Strategies in the Classroom
Collaborative learning strategies offer several benefits in the classroom. By working together, students not only improve their understanding of the material but also develop important social and critical thinking skills.
Improved understanding
Collaborative learning helps students understand material better. When they work together, they explain concepts to each other, which reinforces their own knowledge. This shared learning experience often leads to a deeper grasp of the subject matter.
Enhanced critical thinking
Working in groups encourages students to think critically. They must analyze different viewpoints, discuss various solutions, and evaluate ideas together. This process helps them develop stronger problem-solving skills and a more comprehensive understanding of the topic.
Stronger social skills
Collaborative learning builds important social skills. Students practice communicating clearly, listening to others, and working as a team. These skills are valuable not only in school but also in future careers and everyday life.
Increased engagement
Group activities make learning more interactive and fun. Students are more likely to be engaged and motivated when they are actively participating and working with their peers. This increased engagement can lead to better retention of information and a more enjoyable learning experience.
Greater accountability
In a collaborative setting, each student has a role to play and is responsible for their part of the work. This shared responsibility encourages students to stay on task and contribute to the group’s success, fostering a sense of accountability and teamwork.
12 Collaborative Learning Strategies to Foster Stronger Teamwork
To build stronger teamwork in the classroom, various collaborative learning strategies can be used. These methods encourage students to work together, share ideas, and support each other in achieving common goals.
1. Group discussions
Group discussions involve students talking about a topic or question in small groups. This technique allows students to share their ideas, listen to others, and build a collective understanding of the subject. It helps students articulate their thoughts and learn from diverse perspectives.
How to use it
- Form groups - Divide the class into small groups, typically with 3-5 students each. Make sure the groups are balanced in terms of skills and abilities.
- Assign a topic or question - Provide each group with a topic or question related to the lesson. Make sure it is clear and relevant to what they are learning.
- Set guidelines - Explain how the discussion should be conducted. Encourage students to listen to each other, share their ideas, and build on what others say.
- Monitor progress - Walk around the classroom to listen to the discussions and offer guidance if needed. Ensure that all students are participating and staying on topic.
- Share findings - After the discussion, have each group share their main points or conclusions with the class. This allows students to learn from other groups and see different perspectives.
- Reflect and summarize - End the discussion by summarizing the key points and connecting them to the lesson. Encourage students to reflect on what they learned from the group discussion.
2. Role assignments
Role assignments mean giving each student a specific job or responsibility within the group, such as a leader, recorder, or presenter. By clearly defining roles, each student knows what they are responsible for, which helps the group stay organized and ensures everyone contributes.
How to use it
- Define roles - Decide on the roles needed for the group task. Common roles include leader, note-taker, timekeeper, and presenter. Clearly explain what each role involves.
- Assign roles - Assign a role to each student in the group. Ensure that each student understands their responsibilities and how they contribute to the group’s success.
- Provide guidance - Give students instructions on how to fulfill their roles. For example, the leader might organize the group’s activities, while the note-taker records important points.
- Encourage collaboration - Have students work together, with each member fulfilling their role. Encourage them to support one another and communicate effectively.
- Monitor and support - Observe the groups to ensure that everyone is participating and that the roles are being carried out effectively. Offer help if needed.
- Review roles - After the activity, review how well the roles worked. Discuss with the group what went well and what could be improved for next time.
3. Peer teaching
Peer teaching involves students explaining concepts or lessons to each other. After learning a topic, students take turns teaching their peers about different aspects. This method reinforces their own understanding and builds their communication and teaching skills.
How to use it
- Divide the material - Break the lesson into sections or topics. Each section should be manageable and relevant to the overall lesson.
- Assign topics - Assign each student or pair of students a different section of the material to learn and teach to their peers.
- Prepare to teach - Give students time to study their assigned section and prepare how they will explain it to others. They can use notes, visual aids, or examples.
- Teach peers - Have students present their section to the rest of the class. They should explain the material clearly and answer any questions from their peers.
- Encourage interaction - After each presentation, allow time for questions and discussion. This helps ensure that all students understand the material.
- Provide feedback - Offer feedback on both the teaching process and the content covered. Praise effective explanations and suggest improvements if needed.
- Reflect on learning - After all sections have been taught, review the key points as a class. Discuss what was learned and how peer teaching helped understand the material better.
Read more about different types of graphic organizers for reading, writing, teaching, learning and brainstorming.
4. Project-based learning
Project-based learning requires students to work together on a project that involves creating a final product, such as a presentation, report, or model. This strategy encourages collaboration as students must plan, research, and work together to complete the project, helping them develop teamwork and problem-solving skills.
How to use it
- Choose a project - Select a project that relates to the lesson and requires students to use what they’ve learned. The project should be engaging and challenging but achievable.
- Form groups - Divide students into small groups. Each group will work together on the project, so make sure they are balanced in skills and abilities.
- Define roles and tasks - Assign roles within each group, such as researcher, writer, designer, or presenter. Clearly outline the tasks each role will handle to ensure everyone knows their responsibilities.
- Set goals and deadlines - Establish clear goals for the project and set deadlines for each phase. This helps groups stay on track and manage their time effectively.
- Provide resources and support - Give students the resources they need, such as materials, information, and tools. Offer support and guidance as they work on their project.
- Monitor progress - Check in with each group regularly to see how they are progressing. Offer feedback and help if they encounter any problems.
- Present the projects - Have each group present their project to the class. This allows students to share their work and learn from each other’s projects.
- Reflect and evaluate - After the presentations, reflect on the project process with the class. Discuss what worked well and what could be improved. Provide feedback on both the process and the final product.
5. Think-pair-share
Think-pair-share is a technique where students first think about a question or problem individually. They then pair up with a classmate to discuss their ideas before sharing their thoughts with the whole class. This approach promotes individual thinking, peer interaction, and class-wide sharing of ideas.
How to use it
- Pose a question - Start by asking a clear and relevant question related to the lesson. Make sure it’s something that requires thoughtful consideration.
- Think individually - Give students a few moments to think about their answer or ideas on their own. This allows them to formulate their thoughts without immediate influence from others.
- Pair up - Have students pair up with a classmate. They should share their thoughts and discuss their answers with each other. This step helps them clarify their ideas and hear different perspectives.
- Share with the class - After discussing in pairs, invite pairs to share their ideas or answers with the whole class. This provides an opportunity for students to learn from each other and see a range of viewpoints.
- Facilitate discussion - Encourage a class discussion based on the shared ideas. Ask follow-up questions to deepen the conversation and connect it to the lesson.
- Reflect - Conclude by summarizing the main points and discussing how they relate to the lesson. Encourage students to reflect on what they learned from both their partner and the class discussion.
6. Jigsaw technique
The jigsaw technique divides a topic into several sections. Each student is assigned a different section to learn and then teach to their group. Once each student has taught their part, the group pieces together the complete topic. This method helps students become experts in their section and supports collaborative learning as they share their knowledge.
How to use it
- Divide the topic - Break the topic into several sections or parts. Each section should cover a different aspect of the overall subject.
- Form expert groups - Create small groups where each group is assigned one section of the topic. These groups, called “expert groups,” focus on learning their specific section.
- Research and learn - Have the expert groups study their assigned section. They can use textbooks, articles, or other resources to become knowledgeable about their part of the topic.
- Reform groups - After learning their sections, reform new groups where each member represents a different expert group. These new groups will now have members who are experts on different sections of the topic.
- Share knowledge - In the new groups, each student teaches the other members about their section. This way, all group members learn about each part of the topic from their peers.
- Discuss and integrate - Encourage the new groups to discuss the information and put together the complete picture of the topic. This helps them understand how each part connects to the others.
- Present findings - Have each group present what they’ve learned to the class. This allows everyone to hear about each section and understand the entire topic.
- Reflect - After presentations, discuss the topic as a class. Reflect on what was learned and how the different sections fit together.
7. Collaborative problem-solving
Collaborative problem-solving involves presenting a problem or challenge for the group to solve together. Students discuss and brainstorm possible solutions, working together to reach a consensus. This strategy encourages critical thinking, teamwork, and the application of problem-solving skills.
How to use it
- Present a problem - Start by giving the class a clear, engaging problem or challenge related to the lesson. The problem should be open-ended and require thoughtful discussion.
- Form groups - Divide the students into small groups. Each group will work together to find a solution to the problem.
- Discuss and brainstorm - Have each group discuss the problem and brainstorm possible solutions. Encourage them to consider different approaches and ideas.
- Develop a solution - Ask the groups to choose the best solution from their brainstormed ideas and develop a plan to address the problem. They should outline their reasoning and how their solution will work.
- Present solutions - Have each group present their solution to the class. They should explain their approach and how they arrived at their answer.
- Evaluate and discuss - After all groups have presented, discuss the different solutions as a class. Compare the approaches and consider the strengths and weaknesses of each solution.
- Reflect on the process - Reflect on the collaborative process. Discuss what worked well in the group discussions and what could be improved for future problem-solving activities.
8.Group brainstorming
Group brainstorming is a technique where students generate ideas on a topic together. Students contribute their thoughts and build on each other’s ideas to come up with a variety of solutions or approaches. This method promotes creativity and helps students consider different perspectives.
Explore more group brainstorming strategies to drive innovation.
How to use it
- Introduce the topic - Start by presenting a clear and relevant topic or question for the brainstorming session. Make sure it’s something that encourages creative thinking.
- Form groups - Divide the class into small groups, ideally 3-5 students per group. Each group will brainstorm ideas together.
- Set guidelines - Explain the rules for brainstorming: encourage all ideas, avoid criticism, and build on each other’s thoughts. The goal is to generate as many ideas as possible.
- Brainstorm ideas - Give groups time to discuss and list their ideas. They can use a whiteboard or paper to write down their thoughts as they come up.
- Share ideas - After brainstorming, have each group share their ideas with the class. This allows everyone to see the range of ideas generated and contributes to the overall discussion.
- Discuss and refine - Discuss the ideas as a class. Identify the most promising ones and explore how they can be developed or combined.
- Reflect on the process - Reflect on the brainstorming session. Discuss what worked well and how the group process helped in generating ideas.
Learn more about how to brainstorm effectively with our brainstorming guide.
9. Debates
Debates involve students preparing arguments for or against a particular issue. They work in teams to research and develop their positions before presenting their arguments to the class. This technique enhances teamwork, encourages critical thinking, and improves public speaking skills.
How to use it
- Choose a topic - Select a relevant and engaging topic for the debate. It should be something with clear sides or viewpoints, and relevant to the lesson.
- Divide into teams - Split the class into two or more teams, each representing a different side of the issue. Assign each team a position to argue for or against.
- Research and prepare - Give each team time to research their assigned position. They should gather evidence and prepare arguments to support their side of the debate.
- Set up the debate - Arrange a time for each team to present their arguments. Establish ground rules, such as time limits for speaking and guidelines for respectful communication.
- Hold the debate - Allow each team to present their arguments and respond to opposing points. Encourage students to listen carefully and engage with each other’s ideas.
- Facilitate discussion - After the debate, facilitate a class discussion about the arguments presented. Discuss the strengths and weaknesses of each side and any new insights gained.
- Reflect on the experience - Reflect on the debate process with the class. Talk about what was learned, how the debate helped in understanding the topic, and what could be improved.
10. Peer review
Peer review requires students to evaluate and provide feedback on each other’s work. After completing an assignment, students review their peers’ work and offer constructive criticism. This method helps students improve their work through feedback and fosters a collaborative learning environment.
How to use it
- Set clear guidelines - Explain what students should look for when reviewing their peers’ work, such as clarity, accuracy, and completeness. Provide a checklist or rubric if needed.
- Pair up students - Assign each student a peer to review. Ensure that everyone knows who they will be reviewing and who will be reviewing their work.
- Review work - Have students read and evaluate their peer’s work based on the guidelines provided. They should note strengths and areas for improvement.
- Give feedback - Ask students to provide constructive feedback to their peers. They should offer specific suggestions for how to improve and highlight what was done well.
- Discuss feedback - Allow time for students to discuss the feedback they received and give. This can be done in pairs or small groups, focusing on understanding and applying the feedback.
- Revise and improve - Encourage students to use the feedback to revise and improve their own work. They should consider the suggestions and make changes as needed.
- Reflect on the process - After the peer review, discuss what students learned from giving and receiving feedback. Reflect on how the feedback helped them improve their work and how they can use it in future assignments.
Team building activities
Team building activities are exercises designed to strengthen relationships and improve teamwork among students. Activities such as trust exercises or group games help students build trust, improve communication, and work together more effectively.
How to use it
- Choose an activity - Pick a team-building activity that fits the class size, age, and objectives. Activities should be fun and encourage cooperation, such as problem-solving tasks, games, or challenges.
- Explain the purpose - Start by explaining the goal of the activity. Let students know that the purpose is to improve teamwork and communication, not just to have fun.
- Divide into teams - Split the class into small teams. Make sure the teams are balanced in terms of skills and abilities to ensure everyone can contribute.
- Set up the activity - Provide clear instructions on how the activity will be conducted. Explain the rules and any materials needed.
- Participate and facilitate - Have students complete the activity while you observe and facilitate. Offer guidance and support if needed, but let students take the lead in working together.
- Debrief and discuss - After the activity, gather the class and discuss what happened. Ask students to reflect on how they worked together and what they learned about teamwork.
- Apply lessons learned - Encourage students to apply the teamwork skills they practiced in the activity to their regular classwork. Reinforce the importance of collaboration in achieving common goals.
Collaborative technology tools
Collaborative technology tools include digital platforms like shared documents, online whiteboards, or group chat applications. These tools allow students to work together in real-time or remotely, making it easier to collaborate on projects, share ideas, and provide feedback.
How to use it
- Choose the right tool - Select a collaborative tool that fits your classroom needs. Popular options include online whiteboards, shared document editors, and communication platforms.
- Introduce the tool - Show students how to use the tool. Explain its features and how it can help them work together on tasks or projects.
- Set clear goals - Define what you want students to achieve using the tool. Set clear objectives for how the tool should be used in their collaborative work.
- Form groups - Divide students into small groups, if needed. Each group will use the tool to collaborate on their tasks or projects.
- Provide guidance - Offer support as students begin using the tool. Help them with any technical issues and remind them of best practices for online collaboration, such as clear communication and respecting others’ contributions.
- Monitor progress - Keep track of how students are using the tool. Check in regularly to see how they are collaborating and if they need any help.
- Review and reflect - After the task or project is complete, review how the tool helped with the collaboration. Discuss what worked well and what could be improved for future use.
- Encourage feedback - Ask students to provide feedback on their experience using the tool. This helps in understanding their needs and making improvements.
Best Practices for Implementing Collaborative Learning Strategies
Implementing collaborative learning strategies effectively involves careful planning and execution. Here are some best practices to ensure success:
- Clearly define objectives - Set clear goals for what you want to achieve with collaborative learning. Ensure that the objectives align with your lesson plans and learning outcomes.
- Choose appropriate strategies - Select collaborative learning strategies that fit your classroom’s needs and the specific goals of the lesson. Consider the students’ age, skill level, and the subject matter.
- Organize groups effectively - Form groups that are balanced in terms of skills and abilities. Mix students with different strengths to promote diverse perspectives and equitable participation.
- Provide clear instructions - Explain the tasks and expectations to students clearly. Make sure they understand their roles, responsibilities, and the purpose of the collaborative activity.
- Foster a positive environment - Create a supportive classroom atmosphere where students feel comfortable sharing their ideas and collaborating with others. Encourage respectful communication and teamwork.
- Monitor and support - Observe group interactions and offer support as needed. Provide guidance to help students stay on track and address any challenges they may encounter.
- Use technology effectively - Incorporate collaborative technology tools that enhance group work. Ensure that students are familiar with the tools and can use them effectively.
- Encourage reflection - After collaborative activities, have students reflect on their experience. Discuss what worked well, what could be improved, and how they can apply their learning to future group work.
- Assess and evaluate - Evaluate both the process and the outcomes of the collaborative activities. Use assessments to gauge individual contributions and group effectiveness.
- Provide feedback - Offer constructive feedback on the collaborative process and the results. Recognize achievements and provide suggestions for improvement.
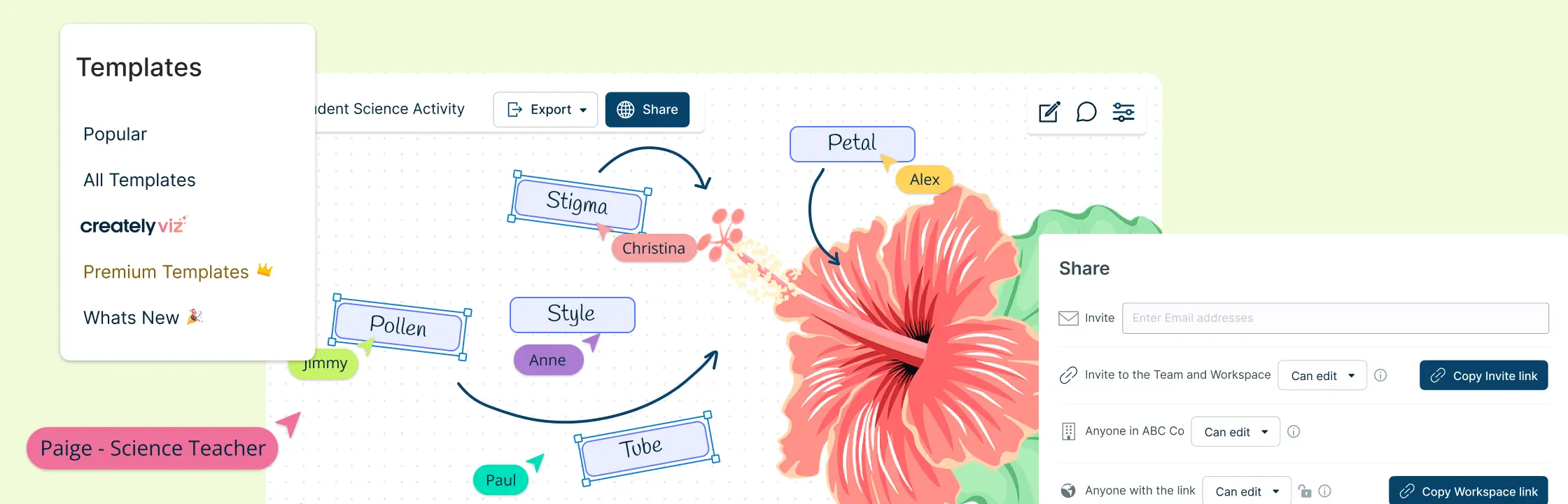
Using Creately for Enhancing Collaborative Learning in the Classroom
Creately is a visual collaboration tool that helps make collaborative learning easier and more effective. Using Creately in the classroom helps students work together more efficiently, share ideas clearly, and manage projects effectively. It makes collaborative learning more interactive and productive.
Interactive Diagrams
Creately allows students to create and edit diagrams together in real-time. They can work on flowcharts, mind maps, and other visual aids, making it easier to brainstorm and organize ideas collectively.
Shared Workspaces
Students can collaborate in shared workspaces, where they can see and edit the same document or diagram simultaneously. This feature ensures everyone is on the same page and can contribute to the project.
Commenting and Feedback
Students and teachers can leave comments on specific parts of the work. This feature helps in providing instant feedback, asking questions, and discussing ideas directly on the document.
Templates and Examples
Creately offers a range of templates for different types of projects, like project planning or SWOT analysis and graphic organizers for writing, reading, note-taking and much more. These templates help students start their work quickly and stay organized.
Easy Integration
Creately integrates with other tools like Google Drive and Microsoft Teams. This makes it easy for students to share their work and collaborate across different platforms.
Real-Time Collaboration
With real-time updates, students can see changes made by their peers immediately. This keeps everyone synchronized and helps in making quick adjustments.
Visual Communication
Creately’s visual tools help in presenting ideas clearly. Students can use charts, diagrams, and other visuals to explain complex concepts more effectively.
Access Control
Teachers can control who can view or edit the documents. This ensures that only authorized members of the group can make changes and helps in managing group work securely.
Conclusion
Collaborative learning strategies can greatly enhance the classroom experience by encouraging teamwork and active participation. Techniques like group discussions, peer teaching, and project-based learning help students learn from each other and build important skills.
To make these strategies effective, set clear goals, choose the right methods, and support students throughout the process. This approach not only improves learning but also helps students develop skills they’ll need in the real world, such as communication and problem-solving. Embracing collaborative learning creates a more engaging and successful educational experience for everyone.
Referneces
Smith, B., Macgregor, J., Goodsell, A., Maher, M. and Tinto, V. (1992). What is collaborative learning? Washington center for improving the quality of undergraduate education what is collaborative learning? *. [online] Available at: https://teach.ufl.edu/wp-content/uploads/2016/07/WhatisCollaborativeLearning.pdf.
Cornell University (2022). Collaborative learning. [online] Center for Teaching Innovation. Available at: https://teaching.cornell.edu/teaching-resources/active-collaborative-learning/collaborative-learning.
Laal, M. and Ghodsi, S.M. (2011). Benefits of Collaborative Learning. Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences, [online] 31(31), pp.486–490. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2011.12.091.
FAQs About Collaborative Learning Strategies
What are the key features of collaborative learning?
How does collaborative learning work?
- Group assignments: The teacher assigns a task that requires teamwork, such as a project, problem-solving activity, or discussion. Each group works together to complete the task.
- Roles and responsibilities: In some cases, students may be assigned specific roles within the group (e.g., leader, note-taker, presenter). This ensures that everyone contributes and the group stays organized.
- Guidance and support: The teacher acts as a facilitator, providing guidance and support when needed, but allowing students to take charge of their learning. The goal is to encourage independence and collaboration among the students.
What is the difference between cooperative vs collaborative learning?
- Cooperative Learning: Involves students working together on a specific task, with each member contributing to achieve a common goal. It often involves structured roles and tasks.
- Collaborative Learning: Focuses on the process of working together to build knowledge and understanding through shared interaction and discussion. It emphasizes mutual learning and shared responsibility.
What is the role of the teacher in collaborative learning?
The teacher’s role in collaborative learning includes:
- Facilitator: Guiding and supporting groups as they work together, ensuring that they stay on task and communicate effectively.
- Planner: Designing and structuring collaborative activities that align with learning objectives.
- Monitor: Observing group interactions and providing feedback to enhance the learning process.
- Mediator: Resolving any conflicts or issues that arise during group work.
- Evaluator: Assessing both the process and the outcomes of collaborative activities to ensure that students meet learning goals.
What are the benefits of collaborative learning?
- Enhances critical thinking: Students discuss various viewpoints, deepening their understanding.
- Improves communication skills: Students practice clear expression and active listening.
- Fosters teamwork: Group work teaches effective collaboration and shared responsibility.
- Builds social skills: Encourages positive interactions and skills like empathy and conflict resolution.
- Increases engagement: Makes learning more dynamic and motivates active participation.
- Enhances problem-solving skills: Promotes creative and strategic thinking through group problem-solving.
- Supports diverse perspectives: Brings together different viewpoints, enriching the learning experience.