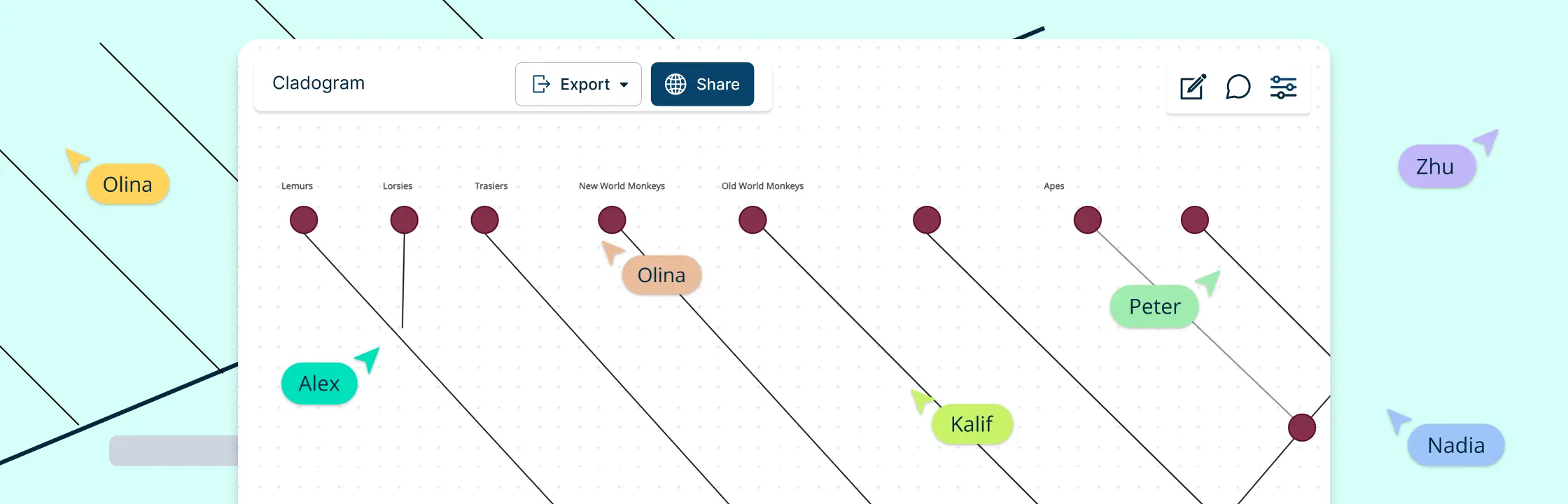
Cladograms are visual tools used by scientists to illustrate the evolutionary relationships among different species. Understanding how to read and interpret these diagrams is crucial for anyone studying evolutionary biology, paleontology, or related fields. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you navigate and understand cladograms.
What is a Cladogram?
Definition and Purpose
A cladogram is a diagram that represents the evolutionary relationships among various biological species based on their physical or genetic characteristics. Essentially, it’s a visual representation of the evolutionary tree of life. The main purpose of a cladogram is to showcase how different species are related through common ancestors. Unlike other classification tools, a cladogram focuses on shared characteristics that derive from common lineage.
Key Components of a Cladogram
Branches: These lines represent the evolutionary path from one ancestor to another. Each branch indicates a divergence, where species split from a common ancestor.
Nodes: These points represent common ancestors shared by the species branching off from that point. Internal nodes (branching points within the diagram) represent ancestral species, while terminal nodes (tips of branches) represent the current species or taxa.
Clades: A clade is a group of organisms that includes an ancestor and all its descendants. It is a single “branch” on the tree of life.
Root: The base of the cladogram, representing the most recent common ancestor of all the organisms in the cladogram.
Examples of Cladograms:
- Primates Cladogram Template:
- Shark to Human Cladogram Template:
- Lemurs to Human Cladogram Template:
Significance of Cladograms in Evolutionary Biology
Understanding evolutionary relationships is crucial in the field of evolutionary biology, and cladograms make this task more accessible. By examining the nodes and branches of a cladogram, scientists can identify the points at which species diverged from common ancestors. This helps in tracing back the evolutionary history and understanding the process of evolution itself.
For instance, a cladogram maker might help you understand the evolutionary pathways that connect various species of birds. The significance of these diagrams extends beyond biology; they’re also instrumental in fields like genetics and paleontology.
Compared to other classification tools such as a phylogenetic tree maker, a cladogram provides a simpler, more focused view of evolutionary relationships. While both tools depict relationships between species, cladograms emphasize shared characteristics, whereas phylogenetic trees incorporate more data points, including the genetic and temporal aspects of evolution.
For anyone looking to delve deeper into comparing these tools, a compare and contrast chart maker can be particularly useful. It highlights the main differences and use cases, making it easier to understand when to use one tool over the other.
In summary, cladograms are invaluable for visualizing the connections between species, thereby aiding in the understanding of evolutionary biology.
How to Read a Cladogram
Steps on How to Read a Cladogram
Identify the Root: Start at the base of the cladogram. This root represents the most ancient common ancestor from which all the organisms in the diagram are descended.
Follow the Branches: Trace the branches from the root towards the tips. Each branching point (node) signifies a common ancestor that diverged into two or more lineages.
Understand Nodes: Nodes represent common ancestors. The closer a node is to the root, the more ancient the common ancestor. Conversely, nodes closer to the tips represent more recent common ancestors.
Examine the Clades: Look for clades, which include a common ancestor and all its descendants. Clades can be nested within larger clades, indicating more distant common ancestry.
Analyze Relationships: To determine the relationship between species, find their most recent common ancestor by tracing back their branches to the nearest shared node. The position of this node indicates how closely related the species are.
How to Read a Cladogram - Example
Let’s take a simple example such as a tree showing the evolutionary relationships between a leopard, a cat, and a wolf. The main line of the cladogram splits into two branches, where one branch represents the common ancestor of cats and the second node further branches into leopards and wolves. This illustration clearly indicates that leopards and wolves share a closer evolutionary relationship with each other than with cats.
Practical Tips
Outgroups: These are species or groups known to be outside the main group of interest and are used to root the cladogram. Identifying outgroups helps in understanding the direction of evolutionary changes.
Synapomorphies: These are shared derived characteristics that help identify clades. Look for these traits to understand which characteristics are used to define each branch.
Homoplasy: Be aware of convergent evolution where different species independently evolve similar traits, which can complicate cladogram interpretation.
How to Make a Cladogram
Creating a cladogram can seem daunting at first, but by breaking it down into manageable steps, you can master the process. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to make a cladogram and how tools like Creately can streamline the effort.
Choosing Organisms
The first step in making a cladogram is selecting the organisms you want to compare. These should be species or groups of organisms that share a common ancestor. For instance, if you’re fascinated by birds, you might choose to compare various species within that category.
Identifying Traits
Next, you need to identify shared and unique traits among the organisms. Traits can range from physical characteristics to genetic markers. Choose characteristics that will help clearly illustrate the evolutionary paths of the organisms.
Organizing Data in a Table
At this stage, it’s helpful to organize your data into a table format. Tools like Creately’s table chart maker can assist you in arranging your data efficiently. Here’s an example table layout:
| Organism | Shared Traits | Unique Traits |
| Species 1 | Trait A, Trait B | Trait D |
| Species 2 | Trait A, Trait B | Trait E |
| Species 3 | Trait A | Trait F |
Drawing the Cladogram
Once your data is organized, you can start drawing your cladogram. Begin with the root, representing the common ancestor, and draw branches to depict evolutionary divergence. Each node represents a point at which species diverged, and the traits identified will help you figure out where to place these nodes.
Using digital tools like Creately’s cladogram maker can significantly simplify this process. With Creately, you can easily drag and drop elements, leverage templates, and collaborate in real-time, making it ideal for educational and group projects.
“Drawing a cladogram by hand can be a meticulous task, but using digital tools can streamline your workflow and enhance your understanding of evolutionary relationships.”
Remember, cladograms are invaluable for tracing the evolutionary history and relationships among species. Leveraging a tool like Creately not only simplifies the creation process but also ensures accuracy and clarity in your diagrams.
Leveraging Digital Tools for Cladogram Creation
Mastering how to read a cladogram becomes more intuitive when using digital platforms. These tools offer interactive features that break down complex information into manageable, visually appealing segments. They bring numerous benefits to the table, especially for educators and students who are keen on collaborative learning. Leveraging digital tools like Creately can significantly enhance the process of creating and reading cladograms. The primary benefits of using digital tools include:
Interactive Visuals: Interactive diagrams make it easier to understand evolutionary relationships and characteristics.
Ease of Access: Cloud-based platforms ensure that work can be accessed and edited from anywhere, at any time.
Version Control: Every change is recorded, enabling users to backtrack and compare different versions of their diagrams.
Advantages of using Creately to read Cladograms
Creately stands out among the digital tools for cladogram creation due to its robust collaboration features. Here are some key capabilities:
Real-time Collaboration: Creately’s platform allows multiple users to work on the same cladogram simultaneously, a feature that is invaluable in group projects and educational settings. Explore more about Creately’s shared editing.
In-app Video Conferencing: Teams can engage in discussions and make decisions on the fly without leaving the platform. This feature mimics in-person collaboration, driving quicker resolutions and insights.
Live Mouse Tracking: Visual cues on the cursor movements of collaborators make following discussions and changes much easier, reducing confusion and enhancing collective understanding.
Interactive diagramming: Easy drag-and-drop functionality to create and adjust branches and nodes.
Creately also offers enterprise-grade security, ensuring that your diagrams and associated data are protected at all times. These features not only enhance collaborative efforts but also streamline the overall workflow, making it more efficient and enjoyable.
Why Choose Creately for Cladograms? Beyond just cladograms, the smart visual canvas from Creately comes equipped with AI-powered tools to transform how teams plan, execute, and collaborate. Whether it’s for project management or educational purposes, Creately provides a unified platform to connect ideas, people, and data seamlessly. Try a demo today and experience the difference!
Conclusion
Reading a cladogram involves understanding the branching patterns and relationships it depicts. By starting at the root, following the branches, and analyzing the nodes and clades, you can decipher the evolutionary relationships among species. Mastering this skill is essential for anyone studying evolutionary biology, providing insights into the shared ancestry and diversification of life on Earth.