Strategic planning is crucial for any business aiming to grow and succeed. To help guide this process, companies use strategic planning frameworks. These frameworks provide a structured approach to defining goals, creating strategies, and ensuring that all efforts align with the company’s vision. In this guide, we will look at 21 strategic planning frameworks that you can use along with templates.
What is a Strategic Planning Framework
A strategic planning framework is a structured method that helps businesses outline their goals, strategies, and actions. It acts as a roadmap, guiding decision-making and ensuring that every aspect of the business is aligned with its overall objectives. This framework helps businesses focus on what’s important, identify opportunities and challenges, and allocate resources effectively to achieve their goals.
Who Can Use Strategic Planning Frameworks
Strategic planning frameworks are versatile tools that can be used by a wide range of businesses and organizations. Here’s who can benefit:
- Small businesses: Helps in setting clear goals and making the most of limited resources.
- Large corporations: Ensures all departments are aligned with the company’s strategic goals.
- Nonprofits: Assists in focusing efforts on mission-driven objectives.
- Startups: Provides a clear direction for growth and helps prioritize efforts.
- Government agencies: Guides in policy-making and resource allocation.
Regardless of size or industry, any organization that wants to grow strategically can benefit from using a strategic planning framework.
Strategic Planning Frameworks vs Strategic Planning Models
The terms “strategic planning frameworks” and “strategic planning models” are often used interchangeably, but they actually refer to different components of the planning process.
Strategic planning models
A strategic planning model outlines the comprehensive structure of your strategic plan. It provides a big-picture view of how all components of your plan connect. The model is established first because it shapes the entire plan’s architecture and direction.
Strategic planning frameworks
Strategic frameworks are used to address specific sections of your strategic plan, providing methods to develop each part in detail. Frameworks are employed to achieve particular goals within the broader plan.
Key differences
- Scope: The model offers a complete view (like seeing the entire forest), while frameworks delve into specific areas (like focusing on individual trees).
- Role: Models establish the structure for the entire strategy, whereas frameworks refine particular aspects within that structure.
- Use: You’ll use one model to organize your strategic plan, but multiple frameworks can be applied to enhance various parts of the strategy.
21 Strategic Planning Frameworks to Achieving Organizational Goals
By providing structured approaches, strategic plannnig frameworks guide businesses in analyzing their environment, identifying opportunities, and executing strategies effectively. In this section, we’ll explore 21 strategic planning frameworks, each offering unique ways to drive organizational growth and achieve long-term objectives.
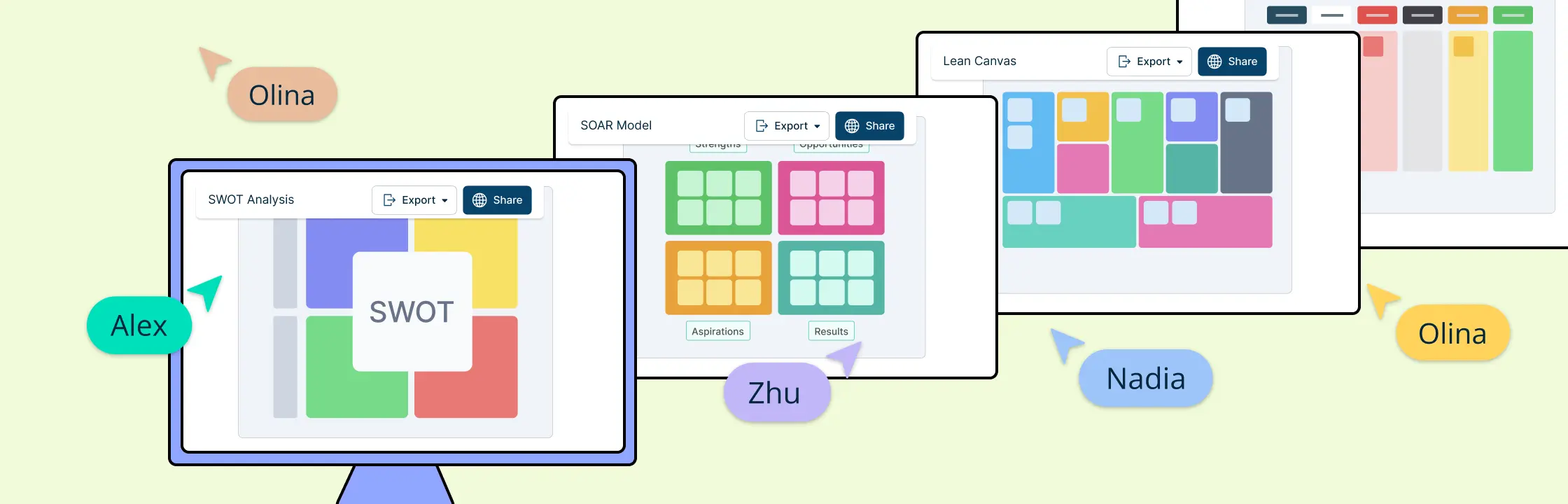
1. SWOT Analysis
SWOT analysis is a strategic planning framework that helps organizations understand their internal and external environments. The name “SWOT” stands for Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats.
What it is: SWOT analysis involves identifying and evaluating an organization’s strengths and weaknesses (internal factors) and opportunities and threats (external factors).
How it’s used: Organizations use SWOT analysis to assess where they stand and to create strategies that leverage their strengths, address their weaknesses, take advantage of opportunities, and protect against threats. This balanced approach ensures that strategic decisions are well-informed and aligned with the organization’s capabilities and the external environment.
2. PESTEL Analysis
PESTLE analysis is a strategic planning framework used to examine external factors that could impact an organization. The acronym “PESTLE” stands for Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Legal, and Environmental factors.
What it is: PESTLE analysis helps organizations understand the broader environment they operate in by evaluating six key areas:
- Political: Government policies and regulations.
- Economic: Economic conditions and trends.
- Social: Societal attitudes and demographics.
- Technological: Technological advancements and innovations.
- Legal: Laws and regulations affecting the industry.
- Environmental: Environmental concerns and sustainability issues.
How it’s used: Organizations use PESTLE analysis to identify potential opportunities and threats in the external environment. This helps them adapt their strategies to align with external changes and make informed decisions to navigate challenges effectively.
3. Porter’s Five Forces
Porter’s five forces is a strategic planning framework that helps organizations understand the level of competition in their industry. The framework examines five key factors that influence competitive intensity:
What it is: Porter’s five forces analyzes:
- Industry rivalry: The degree of competition among existing companies in the industry.
- Threat of new entrants: How easy or difficult it is for new companies to enter the market.
- Bargaining power of suppliers: The influence suppliers have on the prices and quality of materials.
- Bargaining power of buyers: The power customers have to affect prices and quality.
- Threat of substitutes: The likelihood of customers finding alternative products or services.
How it’s used: Organizations use Porter’s five forces to assess the competitive pressures they face. This helps them develop strategies to strengthen their market position, improve their competitive advantage, and address potential threats from competitors, new entrants, and alternative products.
4. Balanced Scorecard
Balanced scorecard is a strategic planning framework that helps organizations track and manage their performance from multiple perspectives. It goes beyond just financial metrics to provide a more complete view of how well the organization is doing.
What it is: The balanced scorecard measures performance across four key areas:
- Financial: Financial outcomes and profitability.
- Customer: Customer satisfaction and market share.
- Internal processes: Efficiency and effectiveness of internal operations.
- Learning and growth: Employee skills, training, and organizational culture.
How it’s used: Organizations use the balanced scorecard to align their day-to-day activities with their long-term goals. By tracking performance in these four areas, they ensure that they are not only achieving financial success but also improving customer satisfaction, streamlining processes, and fostering growth and development within the organization.
5. Growth-Share Matrix (BCG Matrix)
Growth-share matrix or BCG matrix is a strategic planning framework that helps organizations decide how to allocate resources among their products or business units. It classifies them based on their market growth and market share.
What it is: The BCG matrix divides products or business units into four categories:
- Stars: High market share and high growth. These are leaders in a growing market and need investment to maintain their position.
- Cash cows: High market share but low growth. These generate steady revenue with little investment needed.
- Question marks: Low market share but high growth. These require careful analysis to determine if they should be invested in or discontinued.
- Dogs: Low market share and low growth. These are typically candidates for divestment or strategic re-evaluation.
How it’s used: Organizations use the BCG matrix to prioritize their investments. It helps them decide where to invest, which areas to maintain, and which products or units might need to be phased out or restructured, based on their potential for growth and profitability.
6. Ansoff Matrix
Ansoff matrix is a strategic planning framework used to determine growth strategies based on new or existing products and markets.
What it is: The Ansoff matrix outlines four growth strategies:
- Market penetration: Selling more of existing products to existing markets. Focuses on increasing market share.
- Product development: Creating new products for existing markets. Aims to meet changing customer needs or preferences.
- Market development: Introducing existing products to new markets. Targets new customer segments or geographic areas.
- Diversification: Launching new products in new markets. Involves entering entirely new industries or areas.
How it’s used: Organizations use the Ansoff Matrix to choose the best strategy for growth. It helps them evaluate opportunities for expanding their market presence, developing new products, or exploring new market segments. This structured approach supports strategic decision-making to achieve sustainable growth.
7. Porter’s Value Chain
Porter’s Value Chain is a framework used to analyze the steps an organization takes to create and deliver a product or service, aiming to find ways to add value and gain a competitive advantage.
What it is: Porter’s Value Chain breaks down the activities involved in producing and delivering a product into two main categories:
Primary activities: Directly related to creating and delivering the product or service. These include:
- Inbound logistics: Receiving and handling raw materials.
- Operations: The process of transforming materials into products.
- Outbound logistics: Distributing the finished products to customers.
- Marketing and sales: Promoting and selling the products.
- Service: Supporting customers after the sale.
Support activities: Help improve the efficiency and effectiveness of primary activities. These include:
- Procurement: Acquiring the resources needed.
- Technology development: Innovating and improving processes.
- Human resources: Recruiting, training, and managing employees.
- Infrastructure: Organizational systems and management.
How it’s used: Organizations use Porter’s Value Chain to identify where value is added in their processes and where improvements can be made. By analyzing each activity, they can optimize operations, reduce costs, and enhance the overall quality of their product or service, which helps in gaining a competitive edge.
8. Blue Ocean Strategy
Blue Ocean Strategy is a strategic planning framework that encourages organizations to create new markets or “blue oceans” instead of competing in crowded, existing markets or “red oceans.”
What it is: Blue Ocean Strategy focuses on finding untapped market spaces with little or no competition. It’s about innovating and offering unique products or services that stand out and meet new or underserved customer needs.
How it’s used: Organizations use Blue Ocean Strategy to explore and develop new opportunities where they can offer something different from their competitors. By creating value in a new way, they avoid fierce competition and open up new areas for growth, allowing them to attract customers and generate profits in less contested environments.
9. OKRs (Objectives and Key Results)
OKRs is a strategic planning framework that helps organizations set and achieve clear goals by defining specific objectives and measurable results.
What it is: OKRs consist of two parts:
- Objectives: Clear, specific goals you want to achieve. They describe what you want to accomplish.
- Key results: Measurable outcomes that track progress towards the objective. They show how success will be measured.
How it’s used: Organizations use OKRs to set ambitious goals and track their progress. By defining objectives and key results, teams can focus on what’s important, align their efforts, and measure their achievements. This framework helps ensure everyone is working towards the same goals and provides a clear way to monitor performance and drive results. Learn how to create OKRs in more detail with out guide to setting OKRs.
10. Scenario Planning
Scenario planning is a strategic framework used to prepare for possible future changes by exploring different “what-if” scenarios.
What it is: Scenario planning involves imagining several different future situations based on various factors like market trends, economic conditions, or technological advancements. It helps organizations think about how these changes might affect their business.
How it’s used: Organizations use scenario planning to create flexible strategies that can adapt to different possible futures. By considering various scenarios, they can plan responses to potential challenges and opportunities, ensuring they are ready for whatever the future might bring.
11. Gap Analysis
Gap analysis is a strategic planning framework that helps organizations identify the differences between their current performance and their desired goals.
Explore more gap analysis tools.
What it is: Gap analysis involves comparing where the organization currently stands with where it wants to be. It highlights the gaps between current performance and target goals.
How it’s used: Organizations use gap analysis to pinpoint areas where improvements are needed. By identifying these gaps, they can develop action plans to bridge them, ensuring they meet their strategic objectives and improve overall performance.
12. VRIO Analysis
VRIO analysis is a strategic planning framework used to evaluate a company’s resources and capabilities to see if they provide a competitive edge.
What it is: VRIO stands for:
- Value: Does the resource or capability help meet customer needs or solve problems?
- Rarity: Is it something unique or not widely available to competitors?
- Imitability: Is it hard for competitors to copy or recreate?
- Organization: Is the company set up to effectively use this resource or capability?
How it’s used: Organizations use VRIO analysis to understand which resources or capabilities can give them an advantage over competitors. By evaluating these factors, they can focus on strengthening and leveraging their most valuable assets to improve their market position.
13. Lean Canvas
Lean canvas is a strategic planning framework used to quickly outline and test key aspects of a business model.
What it is: Lean canvas is a one-page template that covers essential elements of a business, including:
- Problem: The main issues your product or service aims to solve.
- Customer segments: The specific groups of people or businesses you want to target.
- Unique value proposition: What makes your product or service stand out.
- Solution: How your product or service solves the problem.
- Channels: The ways you will reach and deliver your product to customers.
- Revenue streams: How you will make money.
- Cost structure: The main expenses involved in running your business.
- Key metrics: How you will measure success.
- Unfair advantage: What gives you an edge over competitors.
How it’s used: Organizations use Lean canvas to quickly sketch out and refine their business ideas. It helps them identify key aspects of their business model, test assumptions, and make adjustments based on feedback, leading to more effective and efficient planning.
14. Pareto Analysis
Pareto analysis is a strategic planning framework used to identify and prioritize the most important issues or factors that will have the biggest impact.
What it is: Based on the Pareto Principle, often known as the 80/20 Rule, Pareto analysis helps you find the 20% of causes or problems that contribute to 80% of the results or effects.
How it’s used: Organizations use Pareto analysis to focus their efforts on the most significant problems or opportunities. By identifying the key areas that will have the greatest impact, they can allocate resources more effectively and achieve better results with less effort.
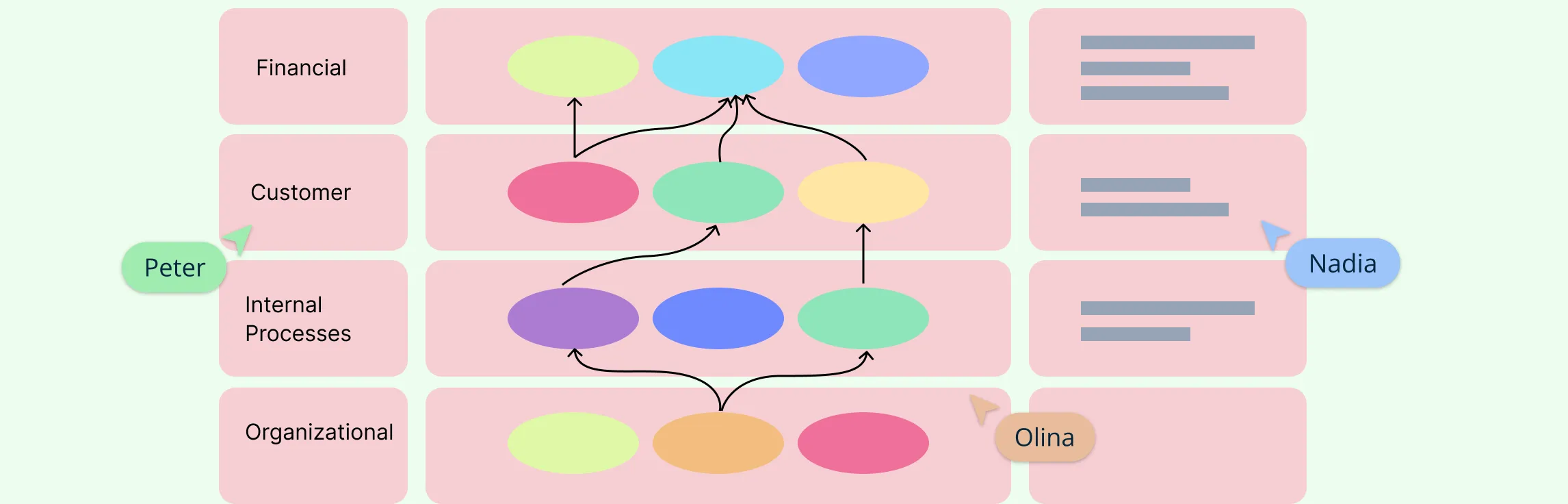
15. Strategy Map
Strategy map is a strategic planning framework that visually outlines an organization’s strategic objectives and how they are connected to achieve its overall goals.
What it is: A strategy map is a diagram that shows the relationships between different strategic goals across four main perspectives:
- Financial: Goals related to financial performance.
- Customer: Objectives focused on customer satisfaction and market positioning.
- Internal Processes: Targets for improving internal processes and efficiency.
- Learning and Growth: Goals related to employee skills, knowledge, and organizational culture.
How it’s used: Organizations use strategy maps to clearly communicate their strategy and how different goals support each other. By visualizing how objectives in each area connect and contribute to overall success, they can ensure alignment across the organization and track progress towards achieving their strategic vision.
16. McKinsey 7-S Framework
McKinsey 7-S framework is a tool used to analyze and align the key elements of an organization to ensure effective strategy implementation.
What it is: The McKinsey 7-S framework examines seven interconnected elements of an organization:
- Strategy: The plan for achieving goals and competitive advantage.
- Structure: The organization’s hierarchy and how roles and responsibilities are arranged.
- Systems: The procedures and processes used to run the organization.
- Shared Values: The core beliefs and culture that guide behavior within the organization.
- Skills: The capabilities and competencies of employees.
- Style: The leadership approach and management style.
- Staff: The organization’s people and how they are recruited, developed, and managed.
How it’s used: Organizations use the McKinsey 7-S framework to ensure all these elements are aligned and support each other. By analyzing and adjusting these areas, they can improve efficiency, adapt to changes, and successfully implement their strategy.
17. SOAR Analysis
SOAR analysis is a framework used to focus on an organization’s strengths and opportunities to create a positive and actionable strategic plan.
What it is: SOAR stands for:
- Strengths: What the organization does well and its key advantages.
- Opportunities: The potential areas for growth and new possibilities in the market.
- Aspirations: The organization’s vision and goals for the future.
- Results: The measurable outcomes and impacts the organization aims to achieve.
How it’s used: Organizations use SOAR Analysis to build on their strengths and opportunities while setting clear goals and desired results. This framework helps in creating a forward-looking, strengths-based strategy that encourages positive growth and aligns efforts with long-term aspirations.
18. Hoshin Kanri
Hoshin Kanri is a strategic planning framework used to align an organization’s strategic goals with its day-to-day operations, ensuring everyone works towards the same objectives.
What it is: Hoshin Kanri, also known as Policy Deployment, involves setting long-term strategic goals and breaking them down into actionable steps. The process includes:
- Setting vision and goals: Define long-term objectives and overall direction.
- Developing strategies: Create plans to achieve these goals.
- Action plans: Break down strategies into specific tasks and responsibilities.
- Monitoring and adjusting: Regularly review progress and make necessary adjustments.
How it’s used: Organizations use Hoshin Kanri to ensure that strategic goals are effectively translated into actionable plans. By aligning all levels of the organization with these goals, it helps improve focus, coordination, and performance, making sure that strategic objectives are consistently pursued and achieved.
19. ADKAR Model
ADKAR model is a framework used to manage and guide organizational change effectively. It focuses on the people side of change to ensure successful transitions.
What it is: ADKAR stands for:
- Awareness: Understanding why the change is needed.
- Desire: Wanting to support and participate in the change.
- Knowledge: Knowing how to change and what new skills are required.
- Ability: Having the capability to implement the change effectively.
- Reinforcement: Ensuring the change is sustained and supported over time.
How it’s used: Organizations use the ADKAR model to guide individuals through change by addressing each of these five areas. It helps in creating a structured approach to managing change, ensuring that people understand, accept, and can effectively implement new strategies or processes.
20. GE-McKinsey Matrix
GE-McKinsey Matrix is a framework used to evaluate and prioritize different business units or products based on their attractiveness and the organization’s strengths.
What it is: The GE-McKinsey Matrix uses two key factors:
- Industry Attractiveness: How appealing the market or industry is, considering factors like growth potential and competition.
- Business Unit Strength: How strong the business unit or product is within the market, based on factors like market share and capabilities.
The matrix divides business units into nine categories, ranging from high attractiveness and strong strength (ideal for investment) to low attractiveness and weak strength (which may need to be divested).
How it’s used: Organizations use the GE-McKinsey Matrix to decide where to allocate resources and make strategic decisions. By evaluating each business unit or product against these criteria, they can focus on areas with the greatest potential for growth and profitability while managing or eliminating weaker areas.
21. Action Plans
Action plan is a strategic planning framework used to outline the specific steps needed to achieve your strategic goals. It breaks down your strategy into manageable tasks with clear timelines.
What it is: An action plan details the who, what, when, and how of your strategy. It includes a list of tasks, deadlines, assigned responsibilities, and resources needed to accomplish each task.
How it’s used: Organizations use action plans to ensure that their strategic goals are turned into actionable steps. By clearly defining each task, setting deadlines, and assigning responsibilities, an Action Plan helps teams stay organized, focused, and on track to achieving their objectives. It provides a clear roadmap for implementing the strategy, making it easier to monitor progress and make adjustments as needed.
Streamline Your Strategic Planning with Creately
Creately is a visual collaboration tool that can make strategic planning easier and more effective. It helps you visualize, collaborate, and manage your strategic planning more effectively, making the entire process smoother and more organized.
Create visual diagrams
- Templates: Use pre-made templates for strategic planning frameworks like SWOT Analysis, PESTEL Analysis, and Value Chain Analysis to quickly get started.
- Drag-and-drop interface: Easily add and arrange elements like shapes, text, and connectors to build custom diagrams.
Collaborate in real-time
- Live editing: Work on your strategic plans simultaneously with team members, seeing changes in real-time.
- Comments and feedback: Add comments directly on the diagrams to provide feedback and discuss ideas without leaving the platform.
Organize information
- Layers and groups: Organize complex information into layers or groups to keep your diagrams clear and manageable.
- Color coding: Use colors to differentiate between various elements or categories in your diagrams.
- Integrated notes and data fields: Attach additional information, attachments, and data with per item notes and data fields to keep everything in the same place.
Track progress
- Interactive charts: Use charts and graphs to visualize data and track progress towards strategic goals.
- Milestones and timelines: Create timelines and milestones to monitor the implementation of your strategies.
- Kanban boards: Use kanban boards and task cards to keep track of tasks and monitor progress. Assign tasks to team members directly within your diagrams, ensuring clear responsibilities.
Share and present
- Export options: Export your diagrams in formats like PDF or PNG to share with stakeholders or include in reports.
- Presentation mode: Use presentation mode to showcase your strategic plans in meetings or presentations.
Conclusion
Strategic planning is essential for guiding your organization toward success. Using different strategic planning frameworks like SWOT Analysis, PESTEL Analysis, and Porter’s Five Forces helps you understand your strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and market conditions.
Each strategic planning framework offers a unique way to analyze your business and make smart decisions. For example, the GE-McKinsey Matrix helps prioritize resources, the Ansoff Matrix explores new market opportunities, and Value Chain Analysis improves operations.
By applying these strategic planning frameworks, you can better prepare for challenges, identify growth opportunities, and stay on track to achieve your goals. Regularly updating your strategies with these tools helps ensure you are always moving in the right direction.