When we think about “design,” we often visualize the end product—the sleek smartphone, the stylish car, or the user-friendly website. However, the design process is much more than just the act of creating visually appealing items. It’s a systematic approach to problem-solving, one that is essential for solving customer problems effectively.
The creative activity of “designing” itself—is the part where we make things look great and function smoothly. But it is only one part of a much larger design process that is a structured journey that takes us from identifying a problem to developing a solution.
The Critical Role of Design in Addressing Customer Needs
At its core, design is the identification of a customer’s need and then working backward to create a solution that addresses it. It’s the vehicle that transforms problems into innovative, user-friendly, and effective products or services. The design process is a structured, methodical way to ensure that we consistently arrive at well-thought-out solutions. It prevents haphazard decision-making and fosters a user-centric approach.
What is the Design Process?
The design process is a comprehensive framework used by designers to create innovative solutions to various problems. It involves a sequence of steps, each playing a vital role in guiding the design journey. It’s a roadmap that helps us navigate a problem that is highly functional and aligned with user needs.
Design is Continuous
The dynamic ecosystem of design is one where feedback and insights from one stage feed into the next. It’s a cyclical process where you may need to revisit previous stages as you gather more information and insights.
The 7 Steps of the Design Process
The design process involves a series of interconnected steps that guide the designer from problem identification to the delivery of a user-focused solution. These seven steps provide a structured framework that ensures a systematic approach to design:
Step 1: Problem Identification and Definition
In this initial phase, the objective is to precisely define the problem that the design aims to solve. It’s all about understanding the issue, its context, and its impact.
To define the problem, start by conducting thorough research. This involves gathering information, analyzing data, and talking to stakeholders. At this stage, it can be very helpful to use visual frameworks like mind maps to visualize the complexity of the issue and create a visual representation of the problem space.
- Clearly articulate the problem statement.
- Understand the context in which the problem exists.
- Identify key stakeholders and their perspectives on the problem.
- Document any existing solutions or attempts to solve the problem.
Step 2: User Research and Empathy
With the problem identified, the next step is to delve into user research to gain a deep understanding of the people you’re designing for.
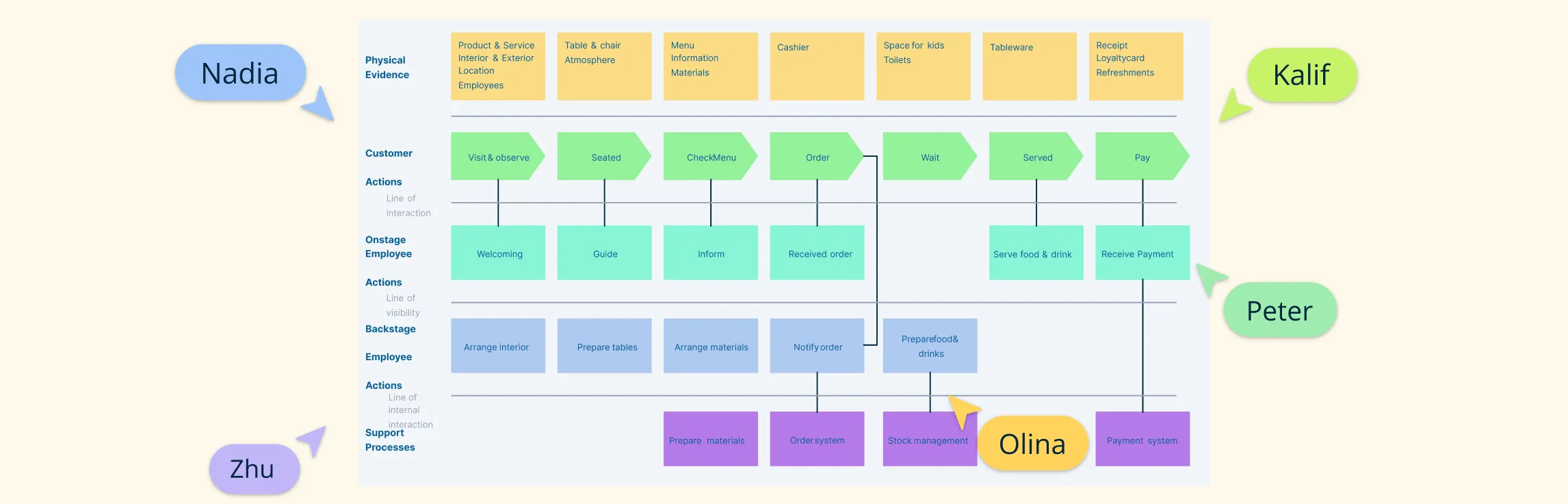
User research involves activities like surveys, interviews, and observation. It’s crucial to understand the needs, behaviors, and pain points of your target audience. User personas, empathy maps, and user journey maps to visualize and document user insights. These insights can then be used to shape the product, design, and user experience. Additionally, they can also help identify potential opportunities for improvement and areas where the user might need additional support.
- Define your target user groups.
- Conduct research through interviews, surveys, and observations.
- Develop user personas to represent typical users.
- Create empathy maps to understand users’ thoughts, feelings, and behaviors.
Step 3: Ideation and Brainstorming
After understanding the problem and your users, it’s time to generate creative solutions.
Ideation involves brainstorming sessions where you and your team generate a wide range of ideas to address the problem. It’s essential to encourage free thinking and creativity during this stage. Techniques like mind mapping, brainstorming sessions, and worst possible idea sessions can help generate a wealth of possibilities.
Things to Keep in Mind:
- Encourage a judgment-free environment to foster creativity.
- Capture all ideas, no matter how wild or unconventional.
- Ensure that team members have diverse backgrounds and perspectives.
- Allow time for individual ideation before group brainstorming.
Step 4: Concept Development and Prototyping
Ideas generated in the previous step need to be shaped into tangible concepts that can be tested. Select the most promising ideas and develop them into concrete concepts. Creating prototypes is a common practice at this stage. Prototypes are simplified representations of the final product or feature. They can be in the form of wireframes, storyboards, or mockups. Prototyping helps to visually represent ideas and gather feedback.
- Focus on the most feasible and impactful concepts.
- Create prototypes that are quick and inexpensive.
- Be open to iterative changes in response to feedback.
- Ensure the prototype represents the user experience.
Step 5: User Testing and Feedback
With the initial design concepts in hand, it’s time to test these with real users and gather feedback. Engage users in testing sessions where they interact with the prototype or concept. Observe their behavior, ask for their input, and collect feedback. Usability testing, A/B testing, and feedback loops are mechanisms that help capture valuable user insights.
- Select a diverse group of users who represent your target audience.
- Establish clear testing goals and tasks for users.
- Be open to criticism and feedback to improve the design.
- Record observations and gather user feedback systematically.
Step 6: Iteration and Refinement
Feedback from users is invaluable in the design process. In this step, you take the feedback and make necessary adjustments. Review the feedback collected during user testing and use it to refine the design. Iterative design is about making incremental improvements based on user input. Design journals are a way to visually document changes and insights during the iterative design process.
- Prioritize changes based on the significance of user feedback.
- Maintain a record of design changes and their reasons.
- Test the refined design with users to verify improvements.
- Continuously refine the design based on user input.
Step 7: Implementation and Launch
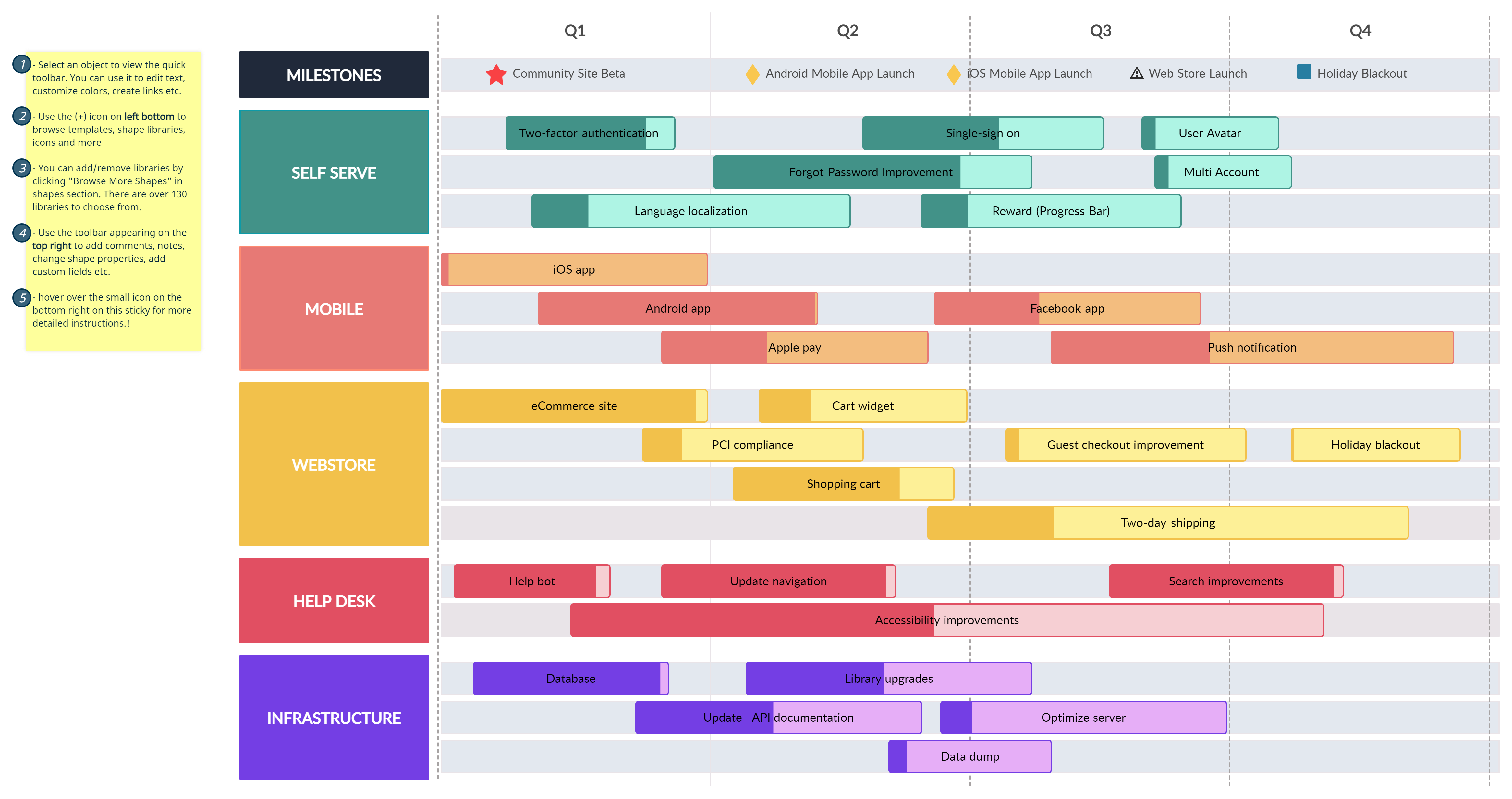
After numerous cycles of feedback and refinement, the design is finally executed, prepared for launch, and delivered to customers. The implementation phase involves translating the design into a final product or service. This requires close collaboration with developers, engineers, or relevant teams. Creating product roadmaps and launch plans can be an effective way to visually communicate goals and milestones for the implementation and launch phase.
- Collaborate closely with development and engineering teams.
- Ensure that the final product aligns with the design vision.
- Communicate the launch plan and milestones clearly.
- Monitor user feedback post-launch for further improvements.
In practice, the design process is not always strictly linear. It often involves moving back and forth between these steps to refine the solution further. An agile approach to design allows for flexibility and adaptation based on real-world feedback and evolving project requirements.
The Importance of User-Focused Thinking Throughout the Process
User-centered design places the user’s needs and experiences at the core of the design process. Every decision made aligns with delivering value to the user. This human-centric approach ensures that designs resonate with real people and provide solutions to their specific problems.
This approach significantly reduces the risk of designing products that miss the mark and leads to enhanced user satisfaction, improved usability, increased engagement, efficient problem-solving, and a superior competitive advantage.
Tips for Enhancing the Effectiveness of the Design Process
1. Foster a Culture of Collaboration: Encourage collaboration and openness within your design team to ensure the free flow of ideas and feedback. This promotes a diverse perspective and enhances the quality of design solutions.
2. Incorporate Regular User Testing: Incorporate regular user testing throughout the design process to catch and address issues early. Early testing allows you to validate your design concepts with real users and make necessary adjustments promptly.
3. Document Design Decisions and Insights: Document design decisions and insights in a clear and organized manner. This documentation helps in knowledge sharing, making informed decisions, and facilitating continuous improvement.
4. Stay Informed About Design Tools and Technologies: Stay knowledgeable about the latest design tools and technologies. The design field is dynamic, and adopting new tools and methods can streamline your design process and make you more efficient.
5. Seek Feedback Continuously: Continuously seek feedback from colleagues and clients to ensure your design process remains effective and adaptable. Constructive criticism and suggestions from others can lead to valuable improvements.